Pressure-sensitive adhesives (PSA) are indispensable bonding materials in modern industry, consumer goods, and high-end manufacturing, widely used in industries such as tapes, protective films, labels, medical dressings, electronics, automotive, aerospace, and aviation. With industrial upgrades and increasing functional requirements, traditional ordinary pressure-sensitive PSAs such as styrene-acrylic, acrylic, and rubber-based adhesives can no longer meet the demands of complex environments, high-performance applications, and specialized industries. What is the difference between silicone pressure-sensitive adhesive?
As a new generation of high-performance PSA materials, silicone pressure-sensitive adhesives are gaining an irreplaceable position in the high-end application market due to their exceptional high and low-temperature stability, superior weather resistance and aging resistance, outstanding adhesive properties, and biocompatibility.
There are six aspects to introducing silicone PSA:
- What is the definition of pressure-sensitive adhesive?
- What are the types of pressure-sensitive adhesives?
- What are the differences between silicone PSA and conventional PSA?
- What are the applications of silicone PSA in high-end markets?
- What are the trends for silicone PSA?
- How to enhance the performance of silicone pressure-sensitive adhesives?
1. What is the definition of pressure-sensitive adhesive?
Pressure-sensitive adhesive (PSA) is a special adhesive that forms a strong bond with the substrate surface under light pressure and ensures minimal residue and damage when removed. It does not rely on water, solvent evaporation, or other chemical reactions and maintains the reversibility of bonding and peeling over the long term.

2. What are the types of pressure-sensitive adhesives?
Non-silicone pressure-sensitive adhesives include:
(1) Rubber-based PSA: Using natural or synthetic rubber as the base material, it has low cost and good adhesion/**strong adhesion**, but poor heat resistance and weather resistance, and is widely used in general-purpose tapes, labels, and other fields.
(2) Acrylic-based PSA: These adhesives primarily use acrylic ester polymers as the main component, offering moderate weather resistance and temperature resistance. They are widely used in the packaging, automotive, and consumer electronics industries.
(3) Water-based or solvent-based PSA: Depending on process environments and environmental requirements, different production processes, such as water-based, solvent-based, or hot-melt types, have been developed.
(4) Silicone pressure-sensitive adhesives:
Silicone pressure-sensitive adhesives use methyl/vinyl/hydrogen-containing siloxane resins (such as MQ, T, or Q-structured silicones) as the core adhesive component, combined with crosslinking agents, tackifiers, release agents, and other components. They are formulated via condensation or addition-curing reactions. Their prominent advantages include high and low temperature resistance, chemical corrosion resistance, UV aging resistance, and moisture and heat resistance.
XJY-301 Silicone pressure-sensitive adhesives
It is made from the specific structure of silicone resin and high molecular weight polydimethylsiloxane in cooperation with organic adhesive, which is suitable for specific scene conditions.
Compared with natural rubber, it is characterized by heat resistance, high stability, good electric insulation, good transparency, high peel adhesion, chemical resistance, etc. It has a wide range of applications in industrial product processing, electronic processing, optical materials, health care, and mica tapes, splicing tapes, protective films other fields.
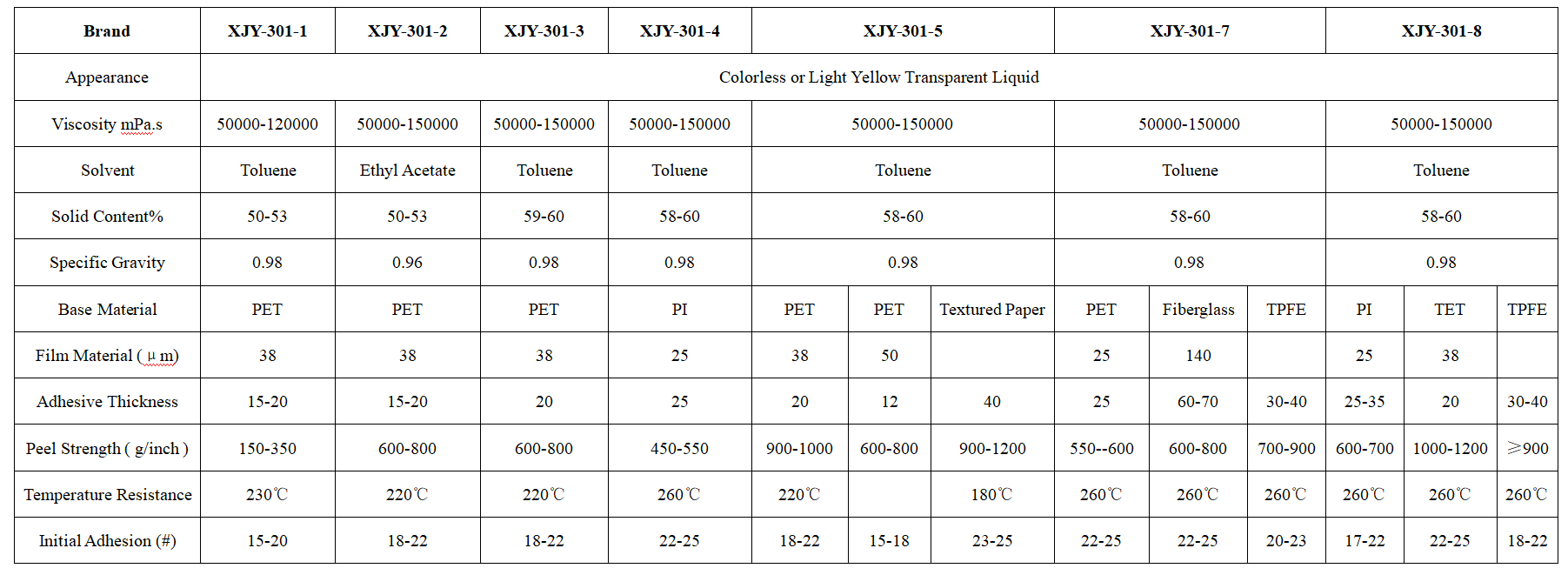
3. What are the differences between silicone PSA and conventional PSA?
(1)Thermal Stability
Conventional PSA: Rubber and acrylic PSA typically only withstand temperatures between -10°C and 80°C (extreme cases up to 120°C), and may lose adhesion, soften, or become brittle in extremely cold or hot environments.
Silicone PSAs: Thanks to the strong thermal stability of the siloxane chain, silicone pressure sensitive adhesive can maintain excellent adhesive properties over a long period in the temperature range of -70°C to 250°C, meeting demands of extreme environments such as aerospace, automotive engines, and electronic packaging, and is widely used for masking tapes, high-temperature films and tapes.

(2) Chemical Resistance
Conventional PSA: It is easily corroded by solvents, acids, alkalis, and oil stains, leading to failure or performance degradation.
Silicone PSA: The high-molecular-weight siloxane main chain and hydrophobic methyl/vinyl side chains enable it to resist most chemical reagents (such as acids, alkalis, solvents, and oils), ensuring long-term reliability and performance.
(3) Weatherability and Aging Life
Conventional PSA: Under the influence of sunlight, ultraviolet rays, and ozone, molecular bonds are prone to breakage, causing the adhesive to yellow, powder, lose adhesion, or migrate.
Silicone pressure sensitive: Possesses excellent UV resistance, antioxidant properties, and ozone aging resistance, typically maintaining stability for 5–20 years without degradation. It is widely used in outdoor protective films, photovoltaic panels, and electrical insulation tapes where aging resistance is required.

(4) Adhesion Flexibility
Conventional PSA: Shows adhesion on polar polymers (e.g., metal, glass, plastic) but has poor adhesion on low energy surfaces (**silicone rubber**, PTFE, PE, PP).
Silicone pressure sensitive adhesive: Demonstrates high peel adhesion and good adhesion on various non-polar, low energy surfaces, making it an excellent choice for “difficult-to-bond substrates” such as silicone rubber, fluoroplastics, and specialty engineering plastics, or where many substrates and different film substrates need to be covered.
(5) Biocompatibility
Conventional PSA: Some formulated systems (e.g., those containing tackifying resins or solvent residues) may cause skin irritation and are unsuitable for skin contact applications or medical use.
Silicone PSAs: High-purity resins are non-toxic and non-irritating, inherently biocompatible, suitable for skin contact applications such as wound dressings, infant care, and medical tapes requiring pain-free removal, and where residue-free removal is a must.
(6) Other Differences
Silicone pressure-sensitive adhesives are moisture-resistant, breathable, and dimensionally stable, with minimal migration, penetration, or elongation, meeting the stringent requirements of electrical insulation tapes, electronic and optical film substrates, and protective films.
Even under extreme conditions such as repeated high/low temperature cycling or intense sunlight, silicone pressure-sensitive adhesives demonstrate consistently high reliability and functional advantages.
4. What are the applications of silicone PSA in high-end markets?
(1) Healthcare sector
Medical dressings and beauty patches: Require long-term adhesion to skin, repeated replacement without causing allergies, and no residue. Silicone pressure-sensitive adhesives are biocompatible and non-irritating, ideal for high-end wound dressings, labels, conductive patches, and skin contact applications such as post-surgical protective films.
Medical tapes and fixation patches: Use for dynamic ECG monitoring, insulin pump fixation, etc., demanding long-lasting adhesion under sweat and high temperature with no damage or residue upon removal.

(2) Electronics and semiconductor industry
Electronic protective films / high-temperature masking tapes: Such as PI film, FPCB protection, and SMT masking, these films can withstand soldering/reflow processes, resist high temp, and leave no residue after removal.
Thermal conductive films and isolation adhesive films: Show good adhesion to many substrates, including aluminum, copper, graphite, and fluoroplastics, used in thermal management for devices such as smartphones and batteries.
(3) Automotive and aerospace
High-temperature masking tapes: Key adhesive application in automotive paint and engine compartments. Aerospace-grade silicone pressure-sensitive adhesive ensures reliability and long-term adhesion.
Lightweight composite bonding: Used for spacecraft protection, cable fixation, and segment transport.
(4) Photovoltaic and new energy
Photovoltaic backsheet protective films/**tape**: Require UV resistance and stability for up to 25 years, suitable for solar cell outer film substrates.
High-temperature bonding for new energy vehicles: Critical for battery module zones, where adhesive properties and high resistance are key.
(5) Industrial and high-end electronics manufacturing
High-frequency/microwave labels, RFID, sensors: For stable adhesion of metals, polymers, and film substrates with long-term performance and signal integrity.
Clean labels, easy-release protective films: Removable, high-purity, and residue-free films and labels for labs and aerospace electronics.
5. What are the trends for silicone PSA?
(1) Rapid expansion of applications in high-end electronics, healthcare, and automotive sectors
As 5G electronics, medical devices, smart products, and new-energy transport continue to expand, requirements for customizable PSA properties rise. Silicone pressure-sensitive adhesives will be a foundation for these markets, supplied in a wide array of formulated types and storage-stable configurations.

(2) Environmental regulations driving upgrades
High-end markets in Europe, the Americas, China, Japan, and South Korea are increasing requirements for non-toxic, low-migration silicone pressure-sensitive adhesive for demanding site conditions, with solvent-free and high-purity resins expected to replace traditional products.
(3) Customization and Industry 4.0 demands
Smart manufacturing and batch precision are accelerating. Jiangxi Xinjia Yi can request and deliver large-scale customization and support complete quality control across all stages, prepared to meet terminal market needs.
(4) Global market growth and import substitution
The global silicone pressure-sensitive adhesive market is growing at around 10% annually, and as domestic technology matures, China will replace imports and also begin exporting high-performance silicone pressure-sensitive materials.
6. How to enhance the performance of silicone pressure-sensitive adhesives?
Silicone pressure-sensitive adhesives, with unmatched resistance to extreme temperature, chemical inertness, dimension stability, biocompatibility, and adhesion to many substrates, are core for modern high-end industry, protective films, electrical insulation tapes, labels, and more. How to further improve competitiveness?
XJY Silicones is one of China's leading manufacturers of organic silicone MQ resins and VMQ silicone rubber, with over 30 years of R&D and manufacturing experience in the silicone industry, as well as over 15 related patents and technical support. Our silicone raw material products can meet the needs of optical and electronic sites, and support diverse, customized solutions for adhesive performance.
![]()




